Great design doesn’t start with visuals. It starts with people. Every project I take on begins with a simple commitment: understand the human on the other side of the screen, the system, or the experience. When you design for real needs, clarity emerges. Complexity becomes manageable. Brands feel more like themselves. And users feel understood.
-
Empowering Humanistic Moments
Design sprint workshops (based on IBM and Google frameworks) enable us to empathize with customer needs, uncover existing pain points, and address new opportunities to transform customer pathways.
-
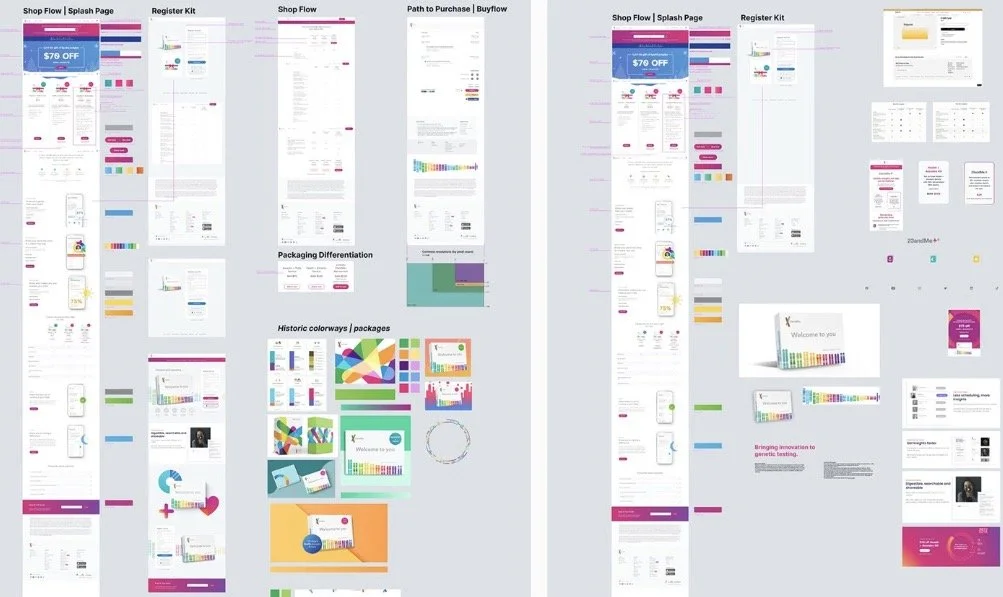
Ideas to Delivery
Communicating customer interactions and design guidelines effectively can be achieved through the visual presentation of information in the form of wireframe conceptualizations, user/process flows, and site mapping.
-
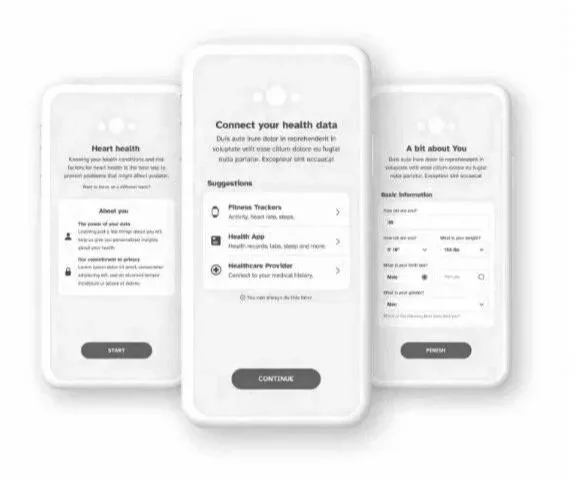
Choose your Journey
User testing, card sorting, and supporting metrics are all valuable tools for measuring the success of a UI. User testing involves observing users as they interact with the UI. Card sorting involves asking users to sort cards with different UI elements into categories. Supporting metrics can include things like time spent on the UI, number of clicks, and number of errors. By following these principles, you can create a good UI that meets the needs of the customer and makes them happy.
-
Reading the Landscape
It is not enough to simply be aware of what your competitors are doing to disrupt the market. One must also be able to identify and capitalize on new trends, as these can provide valuable insights into how to better serve a specific channel or need.
-
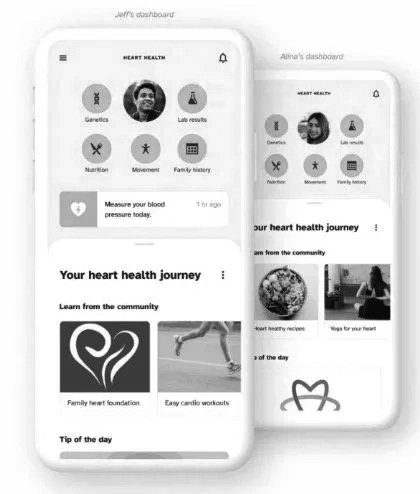
Customer Touch-points
Gaining a thorough understanding of customers' interactions with a product or service allows for the identification of friction points, high-tension areas, and opportunities to define a realistic customer projection.
-
Reshaping impactful touch-points
The strategic integration of customer behaviors and technology is essential for creating seamless user experiences. However, complex user experiences can often break down due to internal organizational shortcomings, such as a weak link in the ecosystem. By creating basic principles, organizations can create seamless user experiences that delight their customers.
-
Emerging Technology Forecasting
Achieving successful innovation is challenging, as it is difficult to address challenges that may or may not exist within our digital landscapes. These challenges could have negative (or positive) impacts on either existing or new market segments that are powered by channel-less customer experiences.
-
Securing Future Readiness
Organizations are advancing technology faster than their people can absorb it. Many rush to ship new tools without rethinking how teams learn, collaborate, or adapt, widening the gap between tech capability and human capacity.
History shows that the winners are not those who automate fastest, but those who adapt fastest. Competitive advantage now stems from distinctly human strengths, including creativity, curiosity, empathy, and agility, which are enabled by leaders who create the conditions for these strengths to flourish.
-
IDENTIFY HARMFUL DESIGN
Behavioral audits systematically examine how actions, decisions, and processes are carried out across digital environments to ensure alignment with organizational goals, policies, and safety or compliance standards. Rather than focusing solely on outcomes, they assess behaviors and patterns of execution, revealing inconsistencies, biases, and systemic gaps that impact culture, fairness, and performance.
Using observation, data analysis, structured checklists, and stakeholder feedback, behavioral audits provide a non-punitive, constructive view into how policies are applied in practice. This approach enables organizations to move from reactive, after-the-fact corrections to proactive, preventative improvements, strengthening consistency, equity, safety, quality, and overall organizational effectiveness within complex digital ecosystems.
-
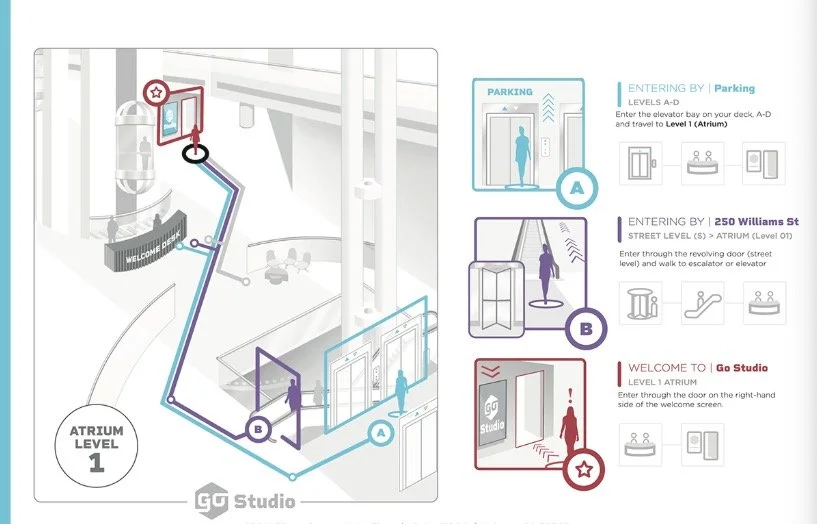
Tiered Visual Insights
Defining the narrative for specific use cases and including a visual component provides opportunities to frame the experience and touchpoints that cannot be captured within prototype renderings.
A narrative is a story that explains a sequence of events. In the context of user experience design, a narrative can be used to describe how a user will interact with a product or service. A visual component can be used to illustrate the narrative and make it more engaging.
By defining the narrative and including a visual component, designers can create a more complete picture of the user experience. This can help to identify potential problems and ensure that the product or service meets the needs of the users.
-
Demographic Representations
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a market into smaller groups based on shared characteristics. This can be done by demographics, such as age, gender, and location, or by psychographics, such as interests, values, and lifestyle. Market segmentation can help businesses to better understand their customers and target their marketing efforts more effectively. It can also help businesses to identify new markets and opportunities.
Market segmentation can be a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes. By understanding their customers and targeting their marketing efforts more effectively, businesses can increase sales and profits.
-
Impacting Customer Motivations
Social networking has become an indispensable part of our lives and businesses. We must rethink the needs of our customers and develop strategies to accurately connect with their niche lifestyles (and our own). We can do this by defining biases and executing trackable and predictive analytics to deliver optimal personalized experiences. We must also present information strategically and efficiently while addressing tension points or barriers and transforming them into opportunity verticals. Finally, we must effectively communicate to the customer a sense of self and responsibility when they experience omnidirectional touchpoints.
-
Cohesion Experience
At the core is the creation of seamless UX/UI touchpoints and fluid information flows that feel effortless yet deeply personalized. By presenting accurate, meaningful content in the right context and at the right moment, brands can transform complexity into clarity. The result is an interface that’s not only easy to use and understand but also responsive, relevant, and engaging, turning every interaction into an opportunity to strengthen customer trust and loyalty. Achieving this requires more than keeping pace with trends and technologies; it demands using them to deliver innovative, intuitive, and human-centered design solutions.
-
Developing Dynamic Strategies
Design sprints thrive on momentum and collaboration. When we come together, we’re able to connect strategies, spark bold ideas, and uncover solutions that wouldn’t emerge in silos. But a sprint doesn’t run on its own—it requires the support of peers, team members, and leadership to truly take flight.
The real value comes when participants are empowered to take risks, voice strong perspectives, and challenge assumptions. That willingness to step forward is what aligns the sprint with our vision, our initiatives, and our priorities.
-
Transformative Platform Automations
Most AI platforms stop at automating routine tasks, but true enterprise transformation demands more. It requires intelligence that understands your business, seamlessly connects people and systems, and drives measurable outcomes. By reimagining AI agents to operate in harmony, organizations can capture intent, trigger actions automatically, and deliver precise, contextual insights through secure, real-time data access. The result is intelligent orchestration across complex, multi-system workflows that accelerate deployments, strengthen compliance, and reduce costs, creating tangible business impact.
-
Defining Advancement Strategies
The ultimate disruptors are those who change the status quo. They are the companies that create new markets and set trends in the landscape of technology and customer lifestyles. Some of the most notable disruptors are changing the world. These companies are not afraid to challenge the status quo and they are constantly innovating. They are the ones who are driving the future.
-
Go-To-Market
A crisp value narrative. Winning GTM motions articulate a defensible point of view on the problem, a differentiated value proposition, and a proof structure that converts skeptics. This narrative is consistent across marketing, sales, partners, and customer success, with message testing baked into campaign and pipeline design.
Best-practice GTM strategies are customer-anchored, cross-functional, operationally disciplined, and empirically managed. They favor clarity over complexity and treat execution as an ongoing system rather than a one-time plan.
-
Enabling Accurate Forecasting
Sustainable revenue management is a digitally enabled, insight-driven capability, not a one-time pricing or sales activity. Leading organizations manage it as a continuous system aligned across data, customer behavior, and operations, with a clear understanding of organizational verticals and how they function seamlessly as a unified whole.
Unified, real-time data forms the foundation, enabling accurate forecasting, faster decision-making, and scenario planning across channels and markets. Fragmented systems constrain margin performance; integrated platforms unlock it.